What is salt in chemistry?
15Jan
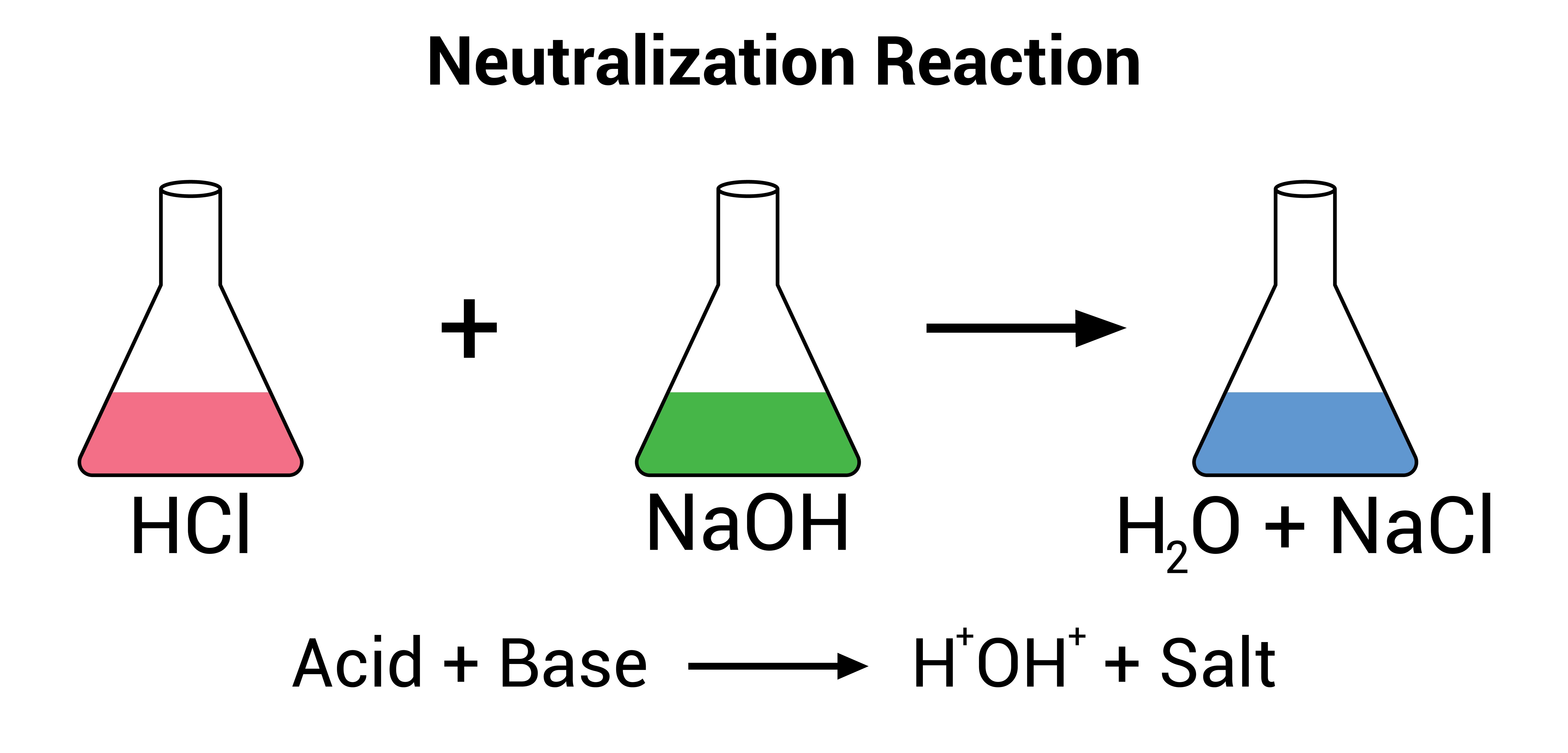
In chemistry, a salt is a compound composed of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions), which are held together by ionic bonds. Salts are formed through the neutralization reaction between an acid and a base. During this reaction, the hydrogen ions (H⁺) from the acid react with the hydroxide ions (OH⁻) from the base to form water, while the remaining ions combine to form the salt
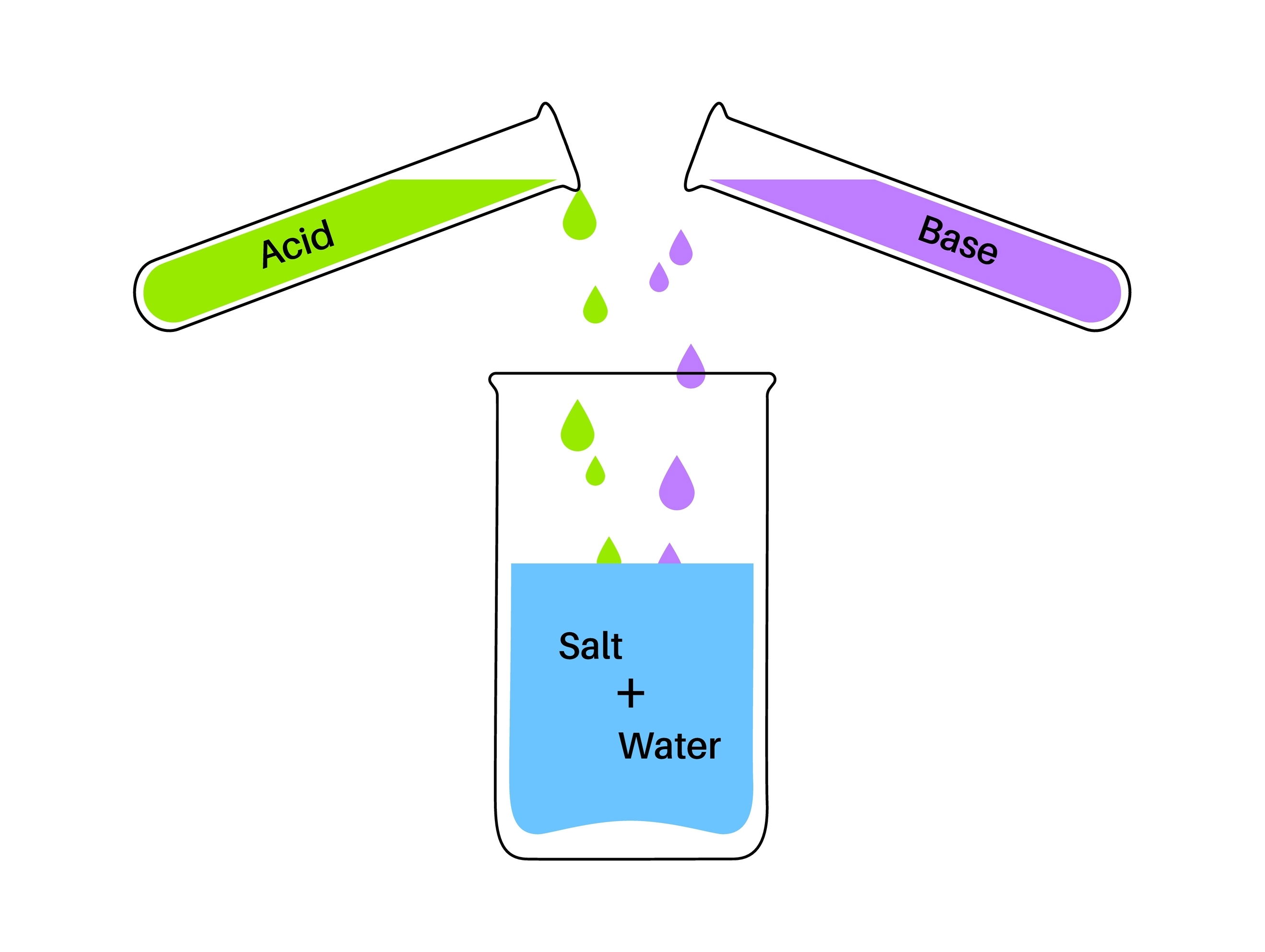
Here are some key points about salts:
- Composition: Salts are typically formed from the reaction between a metal (or ammonium ion, NH₄⁺) and a non-metal (or a polyatomic ion). For example, sodium chloride (NaCl) is formed from the reaction between sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- Ionic Bonding: Salts are held together by ionic bonds, which are formed through the electrostatic attraction between positively and negatively charged ions. In the crystal lattice structure of a salt, the positive ions are surrounded by negative ions, and vice versa.
- Neutral pH: In aqueous solution, salts dissociate into their constituent ions. Depending on the nature of the ions, the resulting solution may be acidic, basic, or neutral. However, most salts formed from the neutralization of strong acids and bases (e.g., NaCl) produce a neutral solution (pH 7).
- Physical Properties: Salts are generally solid at room temperature and have high melting and boiling points. They are often crystalline in structure and may exhibit a range of colors and solubilities in water.
- Uses: Salts have numerous applications in various industries and everyday life. For example, sodium chloride (table salt) is used as a seasoning and preservative in food, as well as in chemical processes such as water softening and the production of chlorine and sodium hydroxide. Other salts are used in agriculture, medicine, and manufacturing processes.
Examples of common salts include:
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Potassium chloride (KCl)
- Calcium carbonate (CaCO₃)
- Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃)
- Magnesium sulfate (MgSO₄)
Understanding salts and their properties is essential in chemistry, as they play significant roles in chemical reactions, solution chemistry, and various industrial processes
Comments